
What is Water Cooling Tower
The Cooling Towers allow water to cool, through thermal and mass exchange, with the atmospheric air of the place.
The most common applications include cooling water circulating in oil refineries, sugar and alcohol plants, chemical industries, power stations, and building cooling.
There are several forms of construction, depending on the manufacturer or the needs of the project.
Cooling water serves to conduct the heat produced by a process to the environment. Normally, the dumping of hot water in canals, rivers, lakes, sea is not allowed, due to the ecological problems that this would cause. In addition, water has become an expensive product and in many applications, extremely expensive. Several reuse methods are then applicable.
The cooling process is characterized by the contact of water with air. So we have an open circuit and a closed circuit.
Open circuit cooling tower
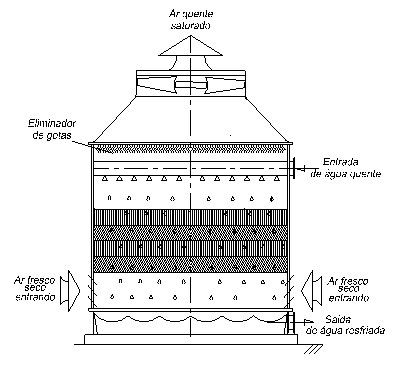
Open circuit – wet cooling. The water in direct contact with the air, transfers through convection and evaporation, heat to the air, a small portion of the water is lost by evaporation.
It is the most economical way of recovering water in circuits where it is used to remove heat from industrial work.
With cooling towers, there is little loss of water, through evaporation, drag, and purge. This system saves electrical energy over a closed circuit or air-cooled ones. The closed-circuit spends about 9% more than the open tower. Air-cooled, about 30% more.
Closed circuit cooling tower
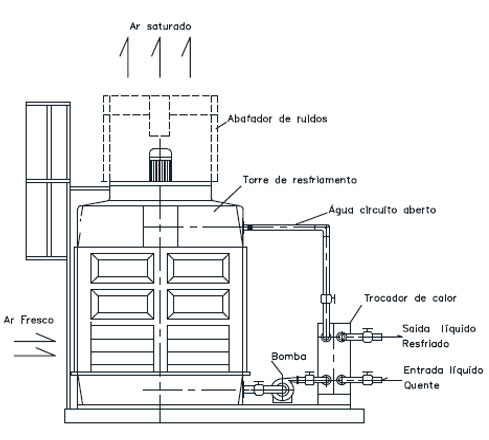
Closed-circuit – dry cooling. There is no contact of water with air. Heat is transferred to the air through tubular or plate heat exchangers. Heat exchange occurs only by convection. Water quality remains constant.
The system used, where the water cannot have contact with the air, so as not to be contaminated. The investment, as well as the operation, is more expensive than in open circuits.


